Marine Protected Area Network Overview
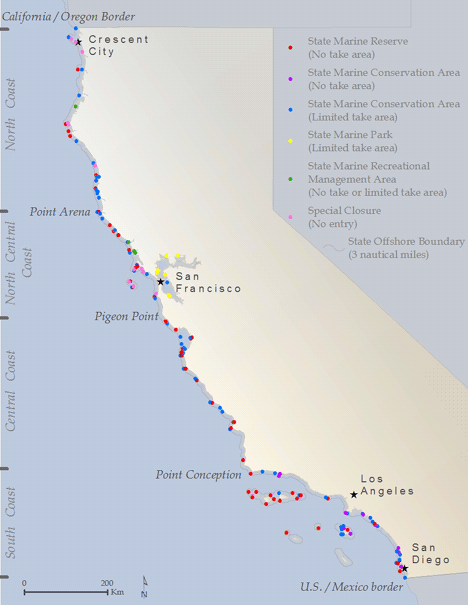
In 2012, California completed a science-based, stakeholder driven process to designate 124 marine protected areas (MPAs) that cover 16% of state waters. The network consists of areas that have various levels of protection, and include some reserves that prohibit all “take.” A full accounting of the design process and statistics for the existing network can be found at the California Department of Fish and Wildlife (CDFW) website. CDFW is charged with the management of the MPA network and is supported by a host of government, non-government and state partners including the Ocean Protection Council (OPC) which is the policy lead for MPAs in the state. Just as our nation’s parks and wilderness areas protect special places on land, California’s MPAs protect a wide array of habitats, species and special places underwater.
Frequently Asked Questions about California’s MPA network.
Key Documents and Resources
- MLPA Master Plan
- MPA Monitoring Program Two-Pager
- MPA Monitoring Data and Reporting
- California Collaborative Approach: MPA Partnership Plan
- MPA Statewide Leadership Team Work Plan
- CNRA Tribal Consultation Policy
- MPA Management Program Report to Legislature January 2016
- Locations of MPA informational signs
Where are California’s MPAs located? CLICK HERE for more information about MPA boundaries.